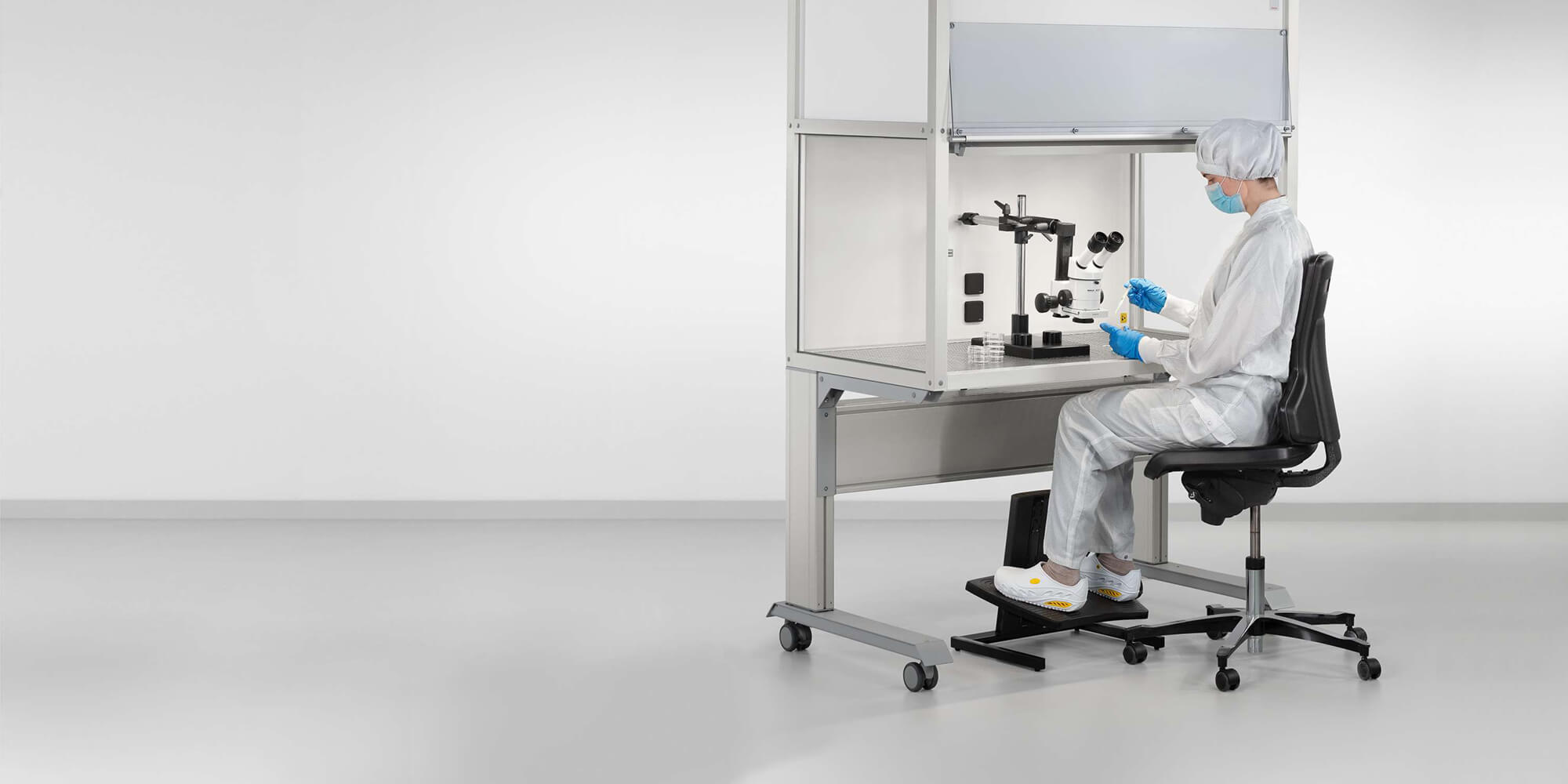
Anybody working with cleanrooms will have to get to grips with a range of cleanroom classes – there’s simply no getting round it.
The coronavirus pandemic made it abundantly clear to everyone that invisible dangers can lurk in the very air around us. However, those dangers aren’t always viruses. Although airborne particles themselves are not harmful, they can pose a very considerable risk for production operations in many sectors. One familiar example is the semiconductor industry, where companies need to protect complex and tiny components from contamination. Even the smallest amount of contamination can be enough to cause malfunctions or failures later on. To make sure this doesn’t happen, production is carried out in cleanrooms, where the number of airborne particles is kept to a set, low level. Cleanroom classes play a key role in standardising these set levels.
All the same, given the various different standards that exist for cleanrooms, it isn’t easy to keep track of requirements. How do the cleanroom classes differ? Which standards are applied when? What is a classification? To make it easier to get started in the world of cleanroom classes, we’re going to answer these and other questions in this blog post. We’ll mainly be exploring two sets of industry rules – the ISO 14644 standard and the EU GMP Guidelines (GMP = Good Manufacturing Practice). We’re happy to share our know-how about cleanroom technology. Our modular building kit system principle is a genuine enabler for bespoke projects, giving you everything you need to design and build dependable cleanroom solutions in precisely the shape, size and configuration you require.

An overview of item solutions for cleanrooms
Whether you’re looking for specialist machine cabins with integrated filter fan units and air recirculation or work benches for clean production, you will find what you are looking for in the range of item products suitable for the manufacture of sensitive products in cleanrooms.
Cleanroom classes to ISO 14644
The ISO 14644 standard applies when the particle count in the air needs to be limited, which is why it is used in technical contexts in the semi-conductor and optics industries, IT and processor technology and the automotive sector, for example. Taking particle concentration per cubic metre (m³) as a metric, ISO 14644 defines nine cleanroom classes – ISO 1 to ISO 9. ISO classes are also known as “air cleanliness classes”. These classes indicate the particle concentration that is permissible in a particular cleanroom. In each class, a maximum permissible particle count per m³ is defined for particle sizes ranging from ≥ 0.1 µm to ≥ 5.0 µm.
Other aspects besides particle concentration are also crucial for a cleanroom solution, such as the type of airflow and how well sealed the structure is.
For example, in an ISO class 1 cleanroom, each m³ must contain no more than just ten particles that are larger than or equal to (≥) 0.1 µm in size and smaller than (<) 0.2 µm. Even the presence of a single particle that is ≥ 0.2 µm in the air will be in contravention of the requirements for cleanroom class ISO 1. By contrast, ISO class 9 permits a total of 35,200,000 particles that are ≥ 0.5 µm in size per m³. Of these, 8,320,000 particles are permitted to be ≥ 1.0 µm in size and 293,000 particles are permitted to be ≥ 5.0 µm in size. In this case, there is no limit on the permissible number of particles that are < 0.3 µm in size. ISO class 1 therefore sets the most stringent air purity requirements, whereas ISO class 9 permits the highest particle load in this narrow framework. You can think of it this way – the higher the ISO class number, the more particles are permissible. However, when creating a cleanroom solution, everything depends on the specific process that will be carried out there. Other aspects besides particle concentration are also crucial for a cleanroom solution, such as the type of airflow and how well sealed the structure is. In this context, classification is about matching a specific process to a particular ISO class based on requirements.
Table of cleanroom classes to ISO 14644
Maximum permissible particle count per m³
| Class | ≥ 0,1 µm | ≥ 0,2 µm | ≥ 0,3 µm | ≥ 0,5 µm | ≥ 1,0 µm | ≥ 5,0 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 1 | 10 | — | — | — | — | — |
| ISO 2 | 100 | 24 | 10 | — | — | — |
| ISO 3 | 1,000 | 237 | 102 | 35 | — | — |
| ISO 4 | 10,000 | 2,370 | 1,020 | 352 | 83 | — |
| ISO 5 | 100,000 | 23,700 | 10,200 | 3,520 | 832 | — |
| ISO 6 | 1,000,000 | 237,000 | 102,000 | 35,200 | 8,320 | 293 |
| ISO 7 | — | — | — | 352,000 | 83,200 | 2,930 |
| ISO 8 | — | — | — | 3,520,000 | 832,000 | 29,300 |
| ISO 9 | — | — | — | 35,200,000 | 8,320,000 | 293,000 |
Source: DIN EN ISO 14644-1

Online training on cleanroom technology and cleanroom classes
Would you like to find out more about cleanrooms? You can find the online training units “Introduction to cleanroom technology” and “Cleanroom technology regulations, focusing on ISO 14644” in the item Academy.
EXPAND YOUR TRAINING NOW
Design custom cleanrooms or utilise sample solutions – with item
When using standard systems, it can be difficult to meet the complex and very specialised requirements in cleanroom technology. The item Building Kit System, however, gives you maximum flexibility and enables you to design a cleanroom that has the dimensions you need and meets your specific requirements. Build custom, walk-in cleanrooms with Fixing System X 8 and Compound Material HPL 36 mm or equip your work bench with a cleanroom-standard enclosure. Work with smooth-surfaced profiles from the start or fit special covers over grooves to close them retrospectively. You can also generate a low-particle airflow by using Filter Fan Units (FFUs). You can read more about the details of individual components and how to build cleanrooms in our blog post on the basics. Are you looking for a ready-made cleanroom solution or just some inspiration? A range of sample solutions can be found in the item Online Shop. Thanks to complete CAD data and parts lists, you can use the sample solutions exactly as they are.
When working at a laminar flow box with a height-adjustable work bench, you can manufacture products efficiently, ergonomically and under cleanroom conditions.
One such sample solution is the machine cabin with Filter Fan Unit and air recirculation. This process enclosure is based on Line XMS profiles with integrated cable conduits and unbroken surfaces. It can generally be certified up to ISO class 2. Line XMS profiles are the ideal basis for building easy-to-clean mini-environments. These are solutions that restrict cleanroom conditions to a distinct, segregated area and a small number of process steps. The Filter Fan Unit provides a high-purity laminar displacement flow in the machine cabin. What’s more, when working at a laminar flow box with a height-adjustable work bench, you can manufacture products efficiently, ergonomically and under cleanroom conditions. The laminar flow box can be certified up to ISO class 5 and is also fitted out with a Filter Fan Unit. Thanks to the flexibility of the item Building Kit System, you can modify the work bench and the enclosure to suit any range of needs. Moreover, it is easy to integrate ESD safety and solutions for supplying materials, stowing tools and displaying information.

Cleanroom grades to EU GMP Guidelines, Annex 1
GMP stands for “Good Manufacturing Practice”. The EU GMP Guidelines set out rules for quality management when manufacturing human and veterinary medicines. You will find the definitions for the different GMP cleanroom classes (referred to as “grades”) in Annex 1 of the guidelines. The cleanroom grades of the EU GMP Guidelines are similar to the ISO classes, as they also factor in particle concentration. However, they additionally set out requirements for avoiding microorganisms and (if relevant) achieving sterility. Another important distinction is that these guidelines differentiate between “at rest” and “operational” states. The EU GMP Guidelines define four grades in total – from A to D, where the strictest requirements apply to grade A and the most relaxed limit values to grade D. In other words, the earlier the cleanroom grade letter comes in the alphabet, the stricter the requirements in terms of cleanliness.
Tables for cleanroom grades to the EU GMP Guidelines
Maximum permissible particle count per m³
| State of rest | Operating state | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | ≥ 0,5 µm | ≥ 5 µm | ≥ 0,5 µm | ≥ 5 µm |
| A | 3,520 | 20 | 3,520 | 20 |
| B | 3,520 | 29 | 352,000 | 2,900 |
| C | 352,000 | 2,900 | 3,520,000 | 29,000 |
| D | 3,520,000 | 29,000 | — | — |
Source: EU GMP Guidelines, Annex 1
Recommended limit values for microbiological contamination (average values)
| Air sample CFU/m3 | Settle plates (diameter 90 mm) CFU/4 hours | Contact plates (diameter 55 mm) CFU/plate | Glove print 5 fingers
CFU/glove |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | ≥ 0,5 µm | ≥ 5 µm | ≥ 0,5 µm | ≥ 5 µm |
| A | < 1 | < 1 | < 1 | < 1 |
| B | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| C | 100 | 50 | 25 | — |
| D | 200 | 100 | 50 | — |
Source: EU GMP Guidelines, Annex 1
Note: CFU = colony forming unit. The number of microorganisms is expressed in CFUs.
An overview of the areas where ISO 14644 and the EU GMP Guidelines are applied
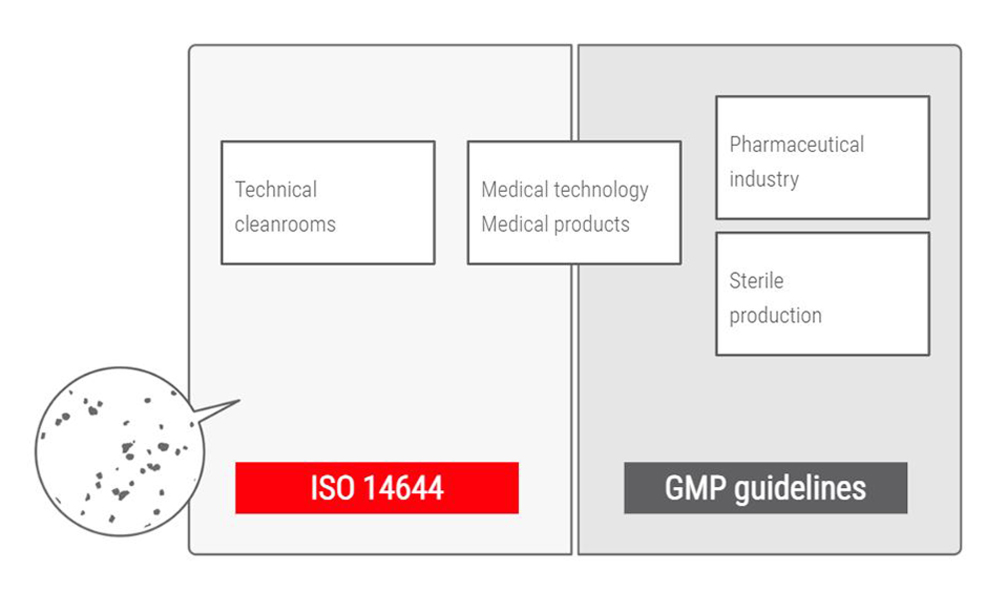
Collated information about cleanrooms
We are always on hand to support your company, whether with products for cleanrooms or expertise about cleanroom technology and technical standards. Below is a collection of links that are relevant to the topic of cleanroom technology. All you need to access the online training courses of the item Academy is an item user account. You can register for one here – it is completely free of charge. Find out more now:
- Online training – “Introduction to cleanroom technology”
- Online training – “Cleanroom technology regulations, focusing on ISO 14644”
- Clean production with item: Overview and e-paper
- Products for cleanrooms in the item Online Shop and sample solutions
- Blog post – “Cleanroom production – modular, flexible solutions”
- Blog post –“Cleanroom: Defining, designing and working in cleanrooms“
Want to keep up to date with everything that’s going on in the world of item? Simply subscribe to the item blog by completing the box at the top right.


